Modern trading is hard to imagine without technical indicators. New traders might be overwhelmed by the sheer number and variety available on their trading platform. However, not all indicators are equally popular among traders. Some are used by almost everyone, while others are quite rare. One of the most widely known and frequently used indicators is the Relative Strength Index (RSI). This article will explain what the RSI is, how to set it up, and how to use it in your trading.
Article content
What is the RSI Indicator?
Let’s start with the basics. The RSI, as the name suggests, measures the relative strength of a price movement. In simpler terms, it analyzes how the price chart moves, gauges the force of up and down movements, calculates their ratio, and displays this information as a line on your chart.
The RSI value ranges from 0 to 100, but in reality, it usually stays between 30 and 70. We’ll discuss why these levels are important a bit later.
Why is RSI So Popular?
Three reasons make the RSI a favorite among traders:
- Easy to Find: You don’t need to download or install anything extra. The RSI is included in MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, and most other trading platforms.
- Simple to Use: Setting up and using the RSI is straightforward.
- Versatile: The RSI works well with various trading strategies.
Setting Up the RSI
If you’re new to the RSI, this quick guide will get you started in seconds. In your trading platform, open the “Indicators” window and go to the “Oscillators” tab. Find the Relative Strength Index there.
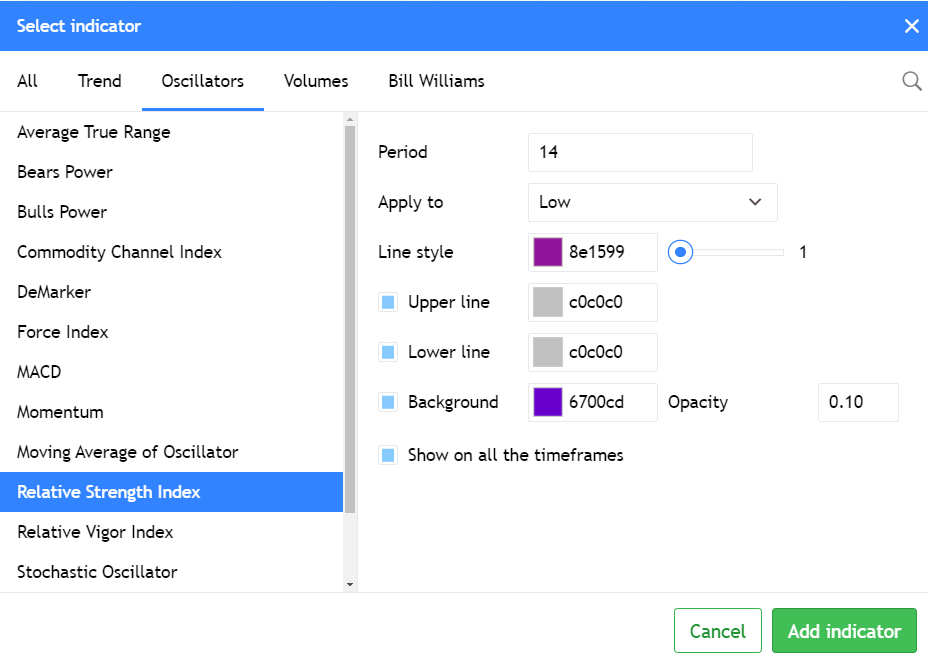
You’ll see a new window where you can configure the RSI.
Feel free to choose line and background colors that work for you. Keep the “Show on all the timeframes” option enabled to avoid having to reconfigure the indicator every time you change your chart timeframe.
The “Period” setting is particularly important. This value tells the RSI how much price history to consider for its calculations. Here’s a general guideline:
- Day Trading: The standard 14-period setting is a good starting point.
- Intraday Trading: For shorter timeframes, a 9-11 period range is more suitable.
- Long-Term Trading: If you plan to hold positions for longer periods and use larger timeframes, you can increase it to 20 or even 30.
However, this is not recommended for beginners. Remember, the higher the timeframe, the less predictable the market becomes due to new information, news events, and other factors. Additionally, you’ll incur extra costs associated with holding positions for longer periods and face the risk of price gaps.
Using the RSI: 30/70 Levels
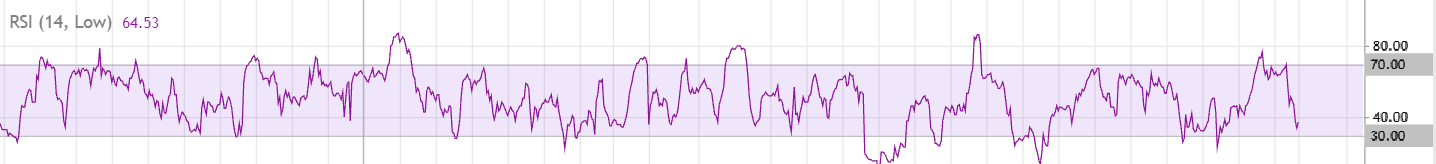
Remember, the RSI helps you identify overbought and oversold zones for an asset. If you examine a long-term chart, you’ll notice the indicator rarely ventures beyond the 30 and 70 levels. And when it does, a reversal often follows shortly after. For instance, the chart below shows the RSI movement on a 1-hour timeframe over two months. Even with over 900 candles, the indicator only goes beyond the 30/70 boundaries 19 times.
Furthermore, after such an excursion, the price typically goes flat or reverses direction altogether:
This is why a popular RSI strategy involves trading reversals based on the indicator crossing above 70 or below 30. It’s important to remember, though, that the RSI can’t predict the future. To strengthen your trading signals, consider combining RSI with recognizable candlestick patterns and analyzing trading volume data. This will increase your chances of success. We also highly recommend practicing on a demo account first. The more experience you gain with RSI, the more trading opportunities you’ll be able to spot.
Spotting Divergence
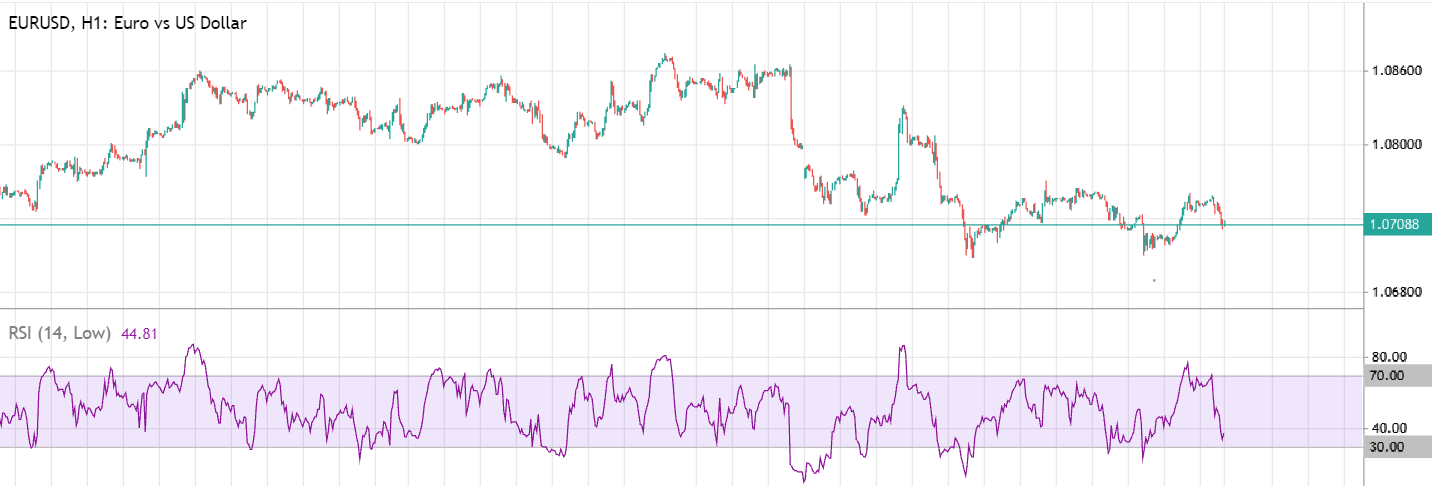
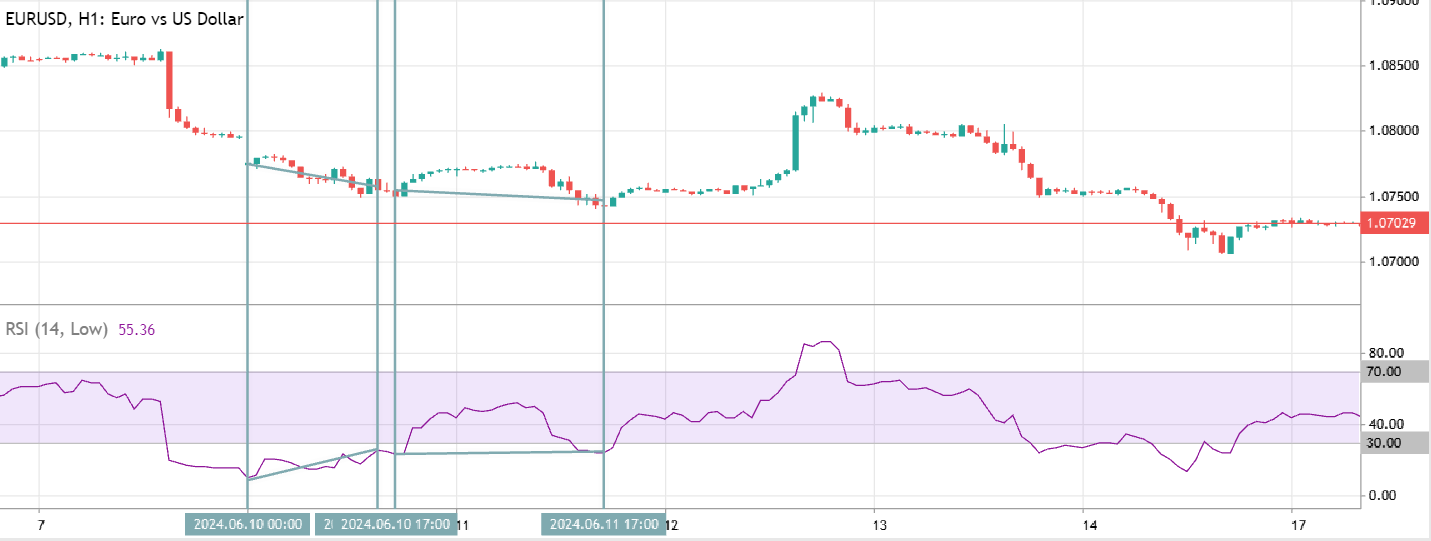
Identifying divergences is another common way to use the RSI. Divergence occurs when the price chart and the RSI line move in opposite directions. For example, in the image below, the EUR/USD currency pair is falling, while the RSI starts to trend upward.
In this case, the indicator dipping below 30 suggests the EUR/USD was oversold, making the signal valid. Shortly after, the pair indeed rose nearly 80 points. There’s also reverse divergence, where rising prices coincide with a downward sloping RSI line.
Conclusion
The RSI remains a favorite among traders due to its simplicity and versatility. It’s easy to set up and offers a range of valuable applications. By using the RSI effectively, you can identify overbought and oversold zones, spot divergences, and make informed trading decisions. However, never forget about risk management, using additional data sources, and honing your skills on a demo account first.